Understanding NoSQL databases
/ 3 min read
One of the first things I remember when I started to understand databases is that I thought there was only one type of non-relational database. Wrong! First of all we have SQL databases, and NoSQL databases. It’s important to understand that they are not a single type of database, but rather categories that encompasses several different types of databases.
Perhaps the most common and the ones we have heard most about are SQL databases, that is why today I am going to talk about NoSQL databases.
NoSQL databases are an alternative to relational databases. They do not use tables and keys like relational databases, but instead use a variety of data structures, such as documents, graphs and key-value pairs. They are highly scalable and offer excellent performance for large unstructured data sets.
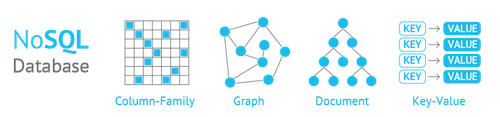
Some of the most popular types of NoSQL databases include:
-
Document databases: These databases store data in the form of documents, such as JSON or XML. Examples of document databases include MongoDB and Couchbase.
-
Key-value databases: These databases store data as a collection of key-value pairs. Examples of key-value databases include Redis (I love this one and I’ve used this for work!) and Riak.
-
Column-family databases: These databases store data in the form of columns, rather than rows. An example of a column-family database is Cassandra.
-
Graph databases: These databases store data in the form of nodes and edges, and are optimized for querying relationships between data. Examples of graph databases include Neo4j and OrientDB.
Differences between NoSQL databases and relational databases
As briefly introduced above, one of the main differences between NoSQL databases and relational databases is the way they handle data. Relational databases, such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, store data in tables with defined schemas. This means that each row in a table must conform to the same structure, and any changes to the schema requires the entire table to be modified.
NoSQL databases, on the other hand, do not have a fixed schema. This means that each document, key-value pair, column, or node can have a different structure. This makes NoSQL databases more flexible and better suited for storing unstructured or semi-structured data.
Another key difference between NoSQL and relational databases is scalability. NoSQL databases are designed to be horizontally scalable, which means they can easily handle large amounts of data and high levels of traffic by adding more servers to the cluster. Relational databases, on the other hand, are typically vertically scalable, which means they can handle more load by adding more resources to a single server.
So… in conclusion?
Okay, okay… In conclusion, we can say that NoSQL databases are a category of non-relational databases that have different characteristics from relational databases. And that they are more flexible, better suited for unstructured or semi-structured data and more horizontally scalable. In certain use cases, like big data or real-time analytics, NoSQL databases may be the better choice.